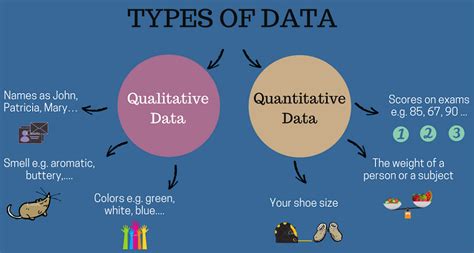
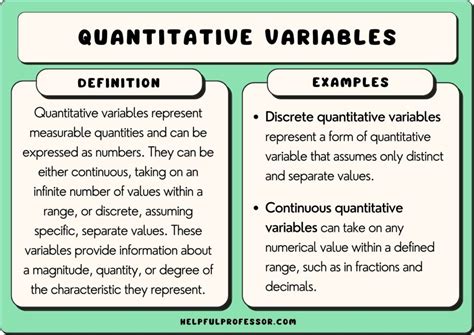
2 quantitative|quantitative variable definition statistics : OEM There are two types of quantitative variables: discrete and continuous. Categorical variables represent groupings of some kind. They are sometimes recorded as .
Provedores. +. Descubra no Clube 777 uma experiência única de cassino com slots vibrantes, roleta e blackjack. Ganhe grandes prêmios em um ambiente seguro e divertido.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBFrei Gilson. Restaurar. A+. Cifra. Tom. + ½. Santo, santo, santo Senhor Deus do universo Senhor Deus do universo Santo, santo, santo Senhor Deus do universo .

what does quantitative data mean
The present guide, which leverages the author’s expertise, experience, and exposure (3Es) in line with Kraus et al. (2022), 1 sheds light on the various dimensions of . Definition: Quantitative variable is a type of variable in statistics that measures a numerical quantity or amount. It is a variable that can be measured on a numeric or . Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data to find patterns, averages, predictions, causal relationships and generalizations. Learn . 1. Quantitative Variables: Sometimes referred to as “numeric” variables, these are variables that represent a measurable quantity. Examples include: Number of students in a class. Number of square feet in a house. .
Quantitative research involves gathering and analysing numerical data to make predictions and describe the relationship between two variables. It deals with more than just numbers and integrates theory, hypothesis, proper . There are two types of quantitative variables: discrete and continuous. Categorical variables represent groupings of some kind. They are sometimes recorded as . In quantitative research, a variable is something (an intervention technique, a pharmaceutical, a temperature, etc.) that changes. There are two kinds of variables: .
Quantitative research is a systematic investigation of phenomena by gathering quantifiable data and performing statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. Quantitative research collects statistically significant information . For example, if someone’s income is twice that of someone else, we can say that their income ratio is 2:1. Quantitative Variable Examples. Here are some examples of quantitative variables: Age: Age is a quantitative variable that can be measured on a continuous scale. It can be measured in years, months, or days.SARS-CoV-2 Total Antibody, Spike, Semi-Quantitative - This test is intended as an aid in identifying individuals with an adaptive immune response to SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), indicating recent or prior infection. The results of this semi-quantitative test should not be interpreted as an indication of degree of immunity or protection from reinfection. 4 CO_Q2_SHS Practical Research 2_Module 1 Lesson Quantitative Research Designs 1 What’s In Quantitative research is more systematic and controlled than qualitative. However, both research methods have a statement of the problem to investigate. At this point, it is assumed that you are already done stating your research problem, the background .
Age is a quantitative variable as it involves counting the number of years a person has lived. Although it can be segmentally measured in units smaller than a year (months, weeks, days, etc.), age is generally reported in complete years, in which case it would be a discrete variable. 2. Height in Centimeters (Continuous Variable) In Chapter 8, we will learn how to estimate the relationship between Beers and BAC after correcting or controlling for those “other variables” using multiple linear regression, where we incorporate more than one quantitative explanatory variable into the linear model (somewhat like in the 2-Way ANOVA). Some of this variability might be hard .2. Quantitative or Qualitative Data can be quantitative or qualitative. One of the most obvious ways to categorize data is by whether it is quantitative or qualitative. Some sources contain either quantitative information or qualitative information, but sources often contain both.
The 2 Main Quantitative Data Analysis Methods. Once you have your data collected, you have to use descriptive statistics or inferential statistics analysis to draw summaries and conclusions from your raw numbers. As its name suggests, the purpose of descriptive statistics is to describe your sample. It provides the groundwork for understanding .3.2 Quantitative Research Designs Quantitive research study designs can be broadly classified into two main groups (observational and experimental) depending on if an intervention is assigned. If an intervention is assigned, then an experimental study design will be considered; however, if no intervention is planned or assigned, then an .
2. Secondary Method. Secondary quantitative research methods involve analyzing existing data that was collected for other purposes. This can include data from government records, public opinion polls, or market research studies. Secondary research is often quicker and less expensive than primary research, but it may not provide data that is as .
This page titled 2.2: Graphing Quantitative Variables is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Foster et al. (University of Missouri’s Affordable and Open Access Educational Resources Initiative) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform.
Quantitative data has a wide range of applications across various fields, including: Scientific research: Quantitative data is used extensively in scientific research to test hypotheses and draw conclusions. For example, in biology, researchers might use quantitative data to measure the growth rate of cells or the effectiveness of a drug treatment.
Find 43 different ways to say QUANTITATIVE, along with antonyms, related words, and example sentences at Thesaurus.com.Chapter 2: Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed Research Lecture Notes This chapter is our introduction to the three major research methodology paradigms. A paradigm is a perspective based on a set of assumptions, concepts, and values that are held and practiced by a community of researchers. For the most of the 20th century the quantitative .CFA Level 2 Quantitative Methods builds on the material covered in Level 1 while emphasizing hypothesis testing. At 5-10% of the exam, Quantitative Methods is one of the less heavily weighted topics. Candidates will become familiar with tools used to identify relationships among variables and examine fintech, machine learning, and sentiment . What is Quantitative Research? Quantitative methodology is the dominant research framework in the social sciences. It refers to a set of strategies, techniques and assumptions used to study psychological, social and economic processes through the exploration of numeric patterns.Quantitative research gathers a range of numeric data.
Quantitative research serves as the cornerstone of evidence-based decision-making. Its importance cannot be overstated: quantitative methods provide empirical rigor, enabling preachers (academia), practitioners (industry), and policymakers (government; i.e. the 3Ps) to derive actionable insights from data. However, despite its significance, mastering the .
quantitative vs qualitative data
Ignore the negative sign and subtract: \(11-9=2\) Give the \(2\) the original sign of the \(-11\) and get \(-2\). Subtraction—Change the sign of the second number, then add, following the rules of addition. It may help if you remember these phrases: Subtracting a negative is the same as adding a positive. A botanist walks around a local forest and measures the height of a certain species of plant. The variable plant height is a quantitative variable because it takes on numerical values. For example, the height could be 15 inches, 17.5 inches, 19.2 .
Two Quantitative Variables: Variable Name Observations (separated by commas or spaces) Keep individuals in the same order. Explanatory: Response: Scatterplot. Calculate Correlation Regression Models Include more detailed regression output Calculate .Herpes Simplex Virus, Type 1 and 2 DNA, Quantitative, Real-Time PCR - The detection of HSV-1 and HSV-2 DNA is based upon the real-time amplification, detection and differentiation of specific HSV-1 and HSV-2 genomic DNA sequences by PCR from total DNA extracted from the specimen. The quantitative range of this assay is 100-2,000,000 copies/mL. Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among variables. This method is widely used in social sciences, psychology, economics, and other fields where researchers aim to understand human behavior and phenomena through statistical analysis. If you are looking for a quantitative .The quantitative HIV2VL assay is used to monitor HIV2 RNA in plasma from known HIV-2 infected patients. This RT-PCR assay targets the Long Terminal Repeat (LTR) region of the HIV-2 genome. Synonyms HIV 2 RNA, HIV 2 Viral Load Components. Code Name; H2DES: HIV_2 Specimen H2RSLT: HIV_2 RNA Result
Bone density in Hounsfield units was assessed using quantitative cone-beam computerized tomography (QCBCT) and quantitative computerized tomography (QCT) in a standardized implant area superimposed on the images. . The Lekholm and Zarb ratings for the 2 examiners showed correlation coefficients ranging between 0.46 and 0.60 for the . Examples of quantitative observation. Quantitative observation is a great starting method to measure the effects of an input on a phenomenon. Example: Quantitative observations of exercise and stress. You are interested in the relationship between exercise and stress levels.. You ask your participants to rate their stress level on a scale of 1-10 (with 10 . Quantitative methods emphasize objective measurements and the statistical, mathematical, or numerical analysis of data collected through polls, questionnaires, and surveys, or by manipulating pre-existing statistical data using computational techniques.Quantitative research focuses on gathering numerical data and generalizing it across groups of people or .
Quantitative and qualitative data provide different outcomes, and are often used together to get a full picture of a population. For example, if data are collected on annual income (quantitative), occupation data (qualitative) could also be gathered to get more detail on the average annual income for each type of occupation.1.2. Foundations of quantitative research methods 1.2.1. Realism, subjectivism and the ‘paradigm wars’ Now we have defined quantitative research, it is a good idea to compare it with qualitative research, to which it is usually put in opposition. While quantitative research is based on numerical data analysed statistically, qual-
Light Transmittance Tester purchase
WEBACESSO AO PEDE FÁCIL. Esqueci minha senha. Gerencie seus pedidos pelo Pede Fácil da Sodexo. Logado, você também consegue acessar sua conta e ficar por dentro de seu saldo Sodexo, extratos e benefícios.
2 quantitative|quantitative variable definition statistics